Traumatic Brain Injury or TBI
TBI or a traumatic brain injury may occur when there is a blow to the head that causes damage to the brain. This “blow” might be penetrating like a gunshot wound. Non-penetrating injuries can include having struck your head in a car accident. When TBI occurs, it can be different in severity depending on the circumstances that led to a traumatic injury of the brain. In many cases, patients can recover within a few days. However, in more severe cases where the possibility of other complications is increased, TBI is also fatal.
According to claims made by the Cleveland clinic, even though anyone can experience a TBI, men make up about 80% of TBI-related cases. A traumatic brain injury has a higher chance of occurrence as the person reaches and passes the age of 65. It is because at this age, the events of the person losing their balance, falling, and hitting their head increase. But, as said earlier in this paragraph, anyone can experience a traumatic brain injury. Even infants can experience a TBI due to incidents such as falling from a bed or changing tables or child abuse in some rare conditions.
Some specific professions or activities tend to increase a person’s chance of getting a TBI, such as athletes despite their level, construction workers, military men and women, police, and law enforcement.
According to the Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), 2014 statistics show that about 3 million people have visited the emergency department due to a TBI. Of all those people, over 54,000 adults and 2,500 children had died because of a traumatic brain injury. It is the sole reason why TBIs or Traumatic Brain Injuries are one of the leading causes of death and disability in the United States of America.
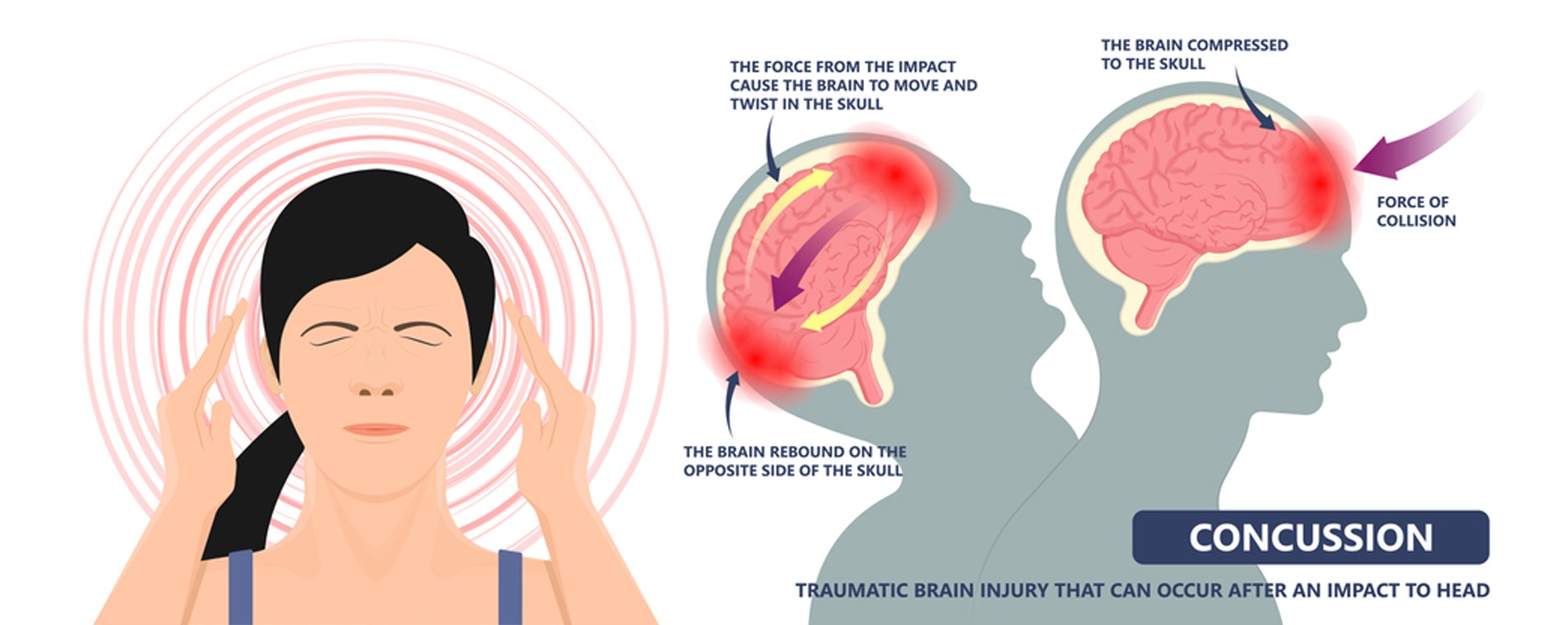
Types of TBI
Several different factors can contribute to determining the severity of the TBI. Factors include loss of consciousness, loss of memory for the injury and time surrounding it, particular neurological symptoms occurring at the time of the damage, abnormalities on head CT or brain MRI, etc. Several types and grades of TBI are known, such as:
Mild TBI: One of the most common types of traumatic brain injuries is a concussion. You could say that 3 out of every 4 cases of TBI are because of concussions. In this type of TBI, the person may experience mild alterations of their consciousness like feeling a loss of consciousness or being dazed for under 30 minutes on average. Confusion is something that people may share with this form of TBI that may last for about a day. Make no mistake that this “confusion” differs from difficulty with attention or memory associated with other types of TBI or other unrelated conditions.
Moderate TBI: In a case of a mild traumatic brain injury, the person might lose consciousness for more than 30 minutes but less than one day. They may also experience confusion, just like in mTBI, but it may last for up to 7 days here.
Severe TBI: People who have this kind of TBI may lose consciousness for over a day. In this form of TBI, injuries caused to the brain are usually associated with changes in head CT or Brain MRI.
Uncomplicated TBI: It is normal to have a mild or moderate TBI after a Head CT or brain MRI.
Complicated TBI: In this form, during the head CT or brain MRI, signs of changes like bleeding can be seen.
Closed: A closed TBI means a blow from the outside has hurt the head. It has not directly opened the skull to affect the inside of the authority. In closed TBI cases, the brain can be injured and caused to swell.
Open: The direct opposite of a closed TBI means the brain has not been damaged directly. In this form of TBI, the brain tissues are damaged because something has penetrated the skull and entered the head. Injuries done using a bullet, knife, or anything that goes through the skull are the main reasons for an open TBI.
Non-traumatic: Sometimes, TBI may not be caused by trauma. Instead, medical conditions such as strokes, seizures, or events such as choking and near-fatal drownings can cause them. These TBIs are also known as hypoxic/anoxic brain injuries. What damaged the brain was the oxygen that was not delivered to the brain.
Symptoms of TBI
When someone experiences a traumatic brain injury, they may show signs and symptoms in both physical and psychological categories. Some might suddenly appear right after the incident that caused the TBI, while others might take days or weeks to show themselves.
Physical symptoms of mTBI may include
- Feeling extremely tired or exhausted
- Speech problems
- Balance loss or dizziness
- Headache
- Nausea or vomiting
Sensory symptoms may include
- Sensitivity to light or sound
- Blurred visions
- Tinnitus – hearing a ring in the ears
- Changes in smelling ability
- A bad taste in the mouth
Psychological or cognitive symptoms may include
- Losing consciousness for about a few seconds up to minutes
- Confusion
- A feeling of being dazed
- Memory problems
- Concentration difficulty
- Mood swings or changes
- Anxiety
- Feeling depressed
- Sleeping difficulty
- Increased sleeping
Moderate and severe traumatic brain injuries symptoms
Any of the signs and symptoms of a mild TBI can also occur in a case of moderate or severe TBI. Some other symptoms may appear suddenly within a few hours up to days after the injury, such as:
Physical:
- Losing consciousness from a couple of minutes up to several hours
- Persistent or progressive headaches
- Repeated vomiting or nausea
- One of both pupils of the eye dilating
- Seizures or convulsions
- Losing the coordination ability
- Fluid drainage from the nose or ears – a clear fluid
- Not being able to wake up from asleep
- Fingers and toes to be numb or weak
Cognitive or psychological symptoms
Intense confusion
Slurry speech
Coma and other disorders regarding consciousness
Agitations, combativeness, or other behaviours that are considered unusual
Children’s symptoms
We said earlier that anyone could experience TBI. However, a child might be so young that they cannot say what their problems are. If they have headaches, sensory issues, confusion, etc., they cannot communicate to say that. Thus, you have to observe some of the following in them:
- Getting easily irritated
- Not being able to pay attention like before
- Not stopping from crying or not being able to console them
- Change in eating or nursing habits
- Change in sleeping habits
- Being sad or in a depressed mood
- Drowsiness
- Not being interested in their favourite toys all of a sudden
How is TBI diagnosed?
A traumatic brain injury can be an emergency, and in a case where the condition is severe, it can worsen quickly every moment it is not receiving treatment. So, TBI needs to be assessed promptly.
Glasgow Coma Scale
Glasgow Coma Scale is a 15-point test that aids the doctor or the ER staff in assessing the severity of TBI by checking the person’s ability to follow directions and move their eyes and limbs. In this test, the point starts from 3 to 15, and a higher score means the condition is less severe.
Information about the injury and symptoms
Even if a witness saw where the patient was injured or arrived exactly after the patient sustained the injury, they can provide the medical personnel with useful information in assessing the patient’s condition. The witness will only have to answer a few questions such as below:
- How were they injured?
- Did they lose consciousness? If yes, how long were they unconscious?
- Did you observe any other changes in alertness, speaking, coordination, or other signs of injury?
- Exactly where on the head or other parts of the body were struck?
Imaging tests
- A CT scan or Computerized Tomography: A CT scan is the first test performed on TBI suspected patients in the ER. Several X-rays will be used in a CT scan test to create a detailed brain image. If any fractures have happened to the brain, it can visualize them and uncover evidence of bleeding in the brain, blood blots, bruised brain tissue, and brain tissue swelling.
- A Magnetic Resonance Imaging or an MRI: During an MRI imaging, mighty radio waves are used along with magnets to produce a detailed image of the brain. The difference between a CT scan and an MRI is that an MRI is used after the patient’s condition has stabilized or if their symptoms are not improving.
Intracranial pressure monitor
If brain tissue gets swollen as a follow-up of a traumatic brain injury, the pressure inside the skull can be increased, leading to additional damage to be done to the brain. A probe will be inserted into the person’s head to monitor it.
Traumatic Brain Injury treatment
If the person’s condition is a mild or moderate TBI, they may not require any more than a minimal treatment like taking a short rest from working out, school, or work. Then, within a few weeks of injury, the symptoms will improve and fade away eventually. However, this is not the case in severe TBI cases. In these cases, they need to be admitted to the hospital and receive hospital care and intense treatments. But, if we take a general look at things, here’s the treatment you may receive despite your grade of TBI.
- Surgery may be used to treat intracranial hemorrhage, also known as bleeding in the brain. Or to reduce the increased pressure because of brain swelling.
- Counselling is used for emotional support. Some people might experience high-stress levels, worry about their recovery from TBI, and find returning to work and their hobbies rather tricky. Thus, counselling will be beneficial when combined with other treatments.
- Rehabilitation such as physical, occupational, and speech therapy can be helpful to victims of more severe TBI cases.
- In less severe cases, you may be ordered to take a rest from other life activities that can drain you from energy, thus, affecting your recovery. You may need about 1 or 2 days of resting if your condition is not serious, but severe cases of TBI may require more extended rest periods.
The focus of treatment is on improving the symptoms and quality of life. In some cases, it may take longer until some symptoms improve, even up to years, for severe head injuries.
Conclusion
You have a moderate or severe TBI that can permanently damage your brain and cause other disabilities. It can cause conditions such as anxiety, depression, PTSD, bleeding in the brain, and epilepsy seizures. In rare cases with very severe injuries to the head, the person’s risk of developing a condition like dementia or Alzheimer’s disease, or even movement disorders is increased. Additionally, these severe complications may follow a potent and rare type of TBI and do not happen with a mild TBI. Contact your doctor if you experienced a traumatic incident such as a car accident where you hit your head, and suddenly you are having symptoms after a few days. Please look at some of the other published content and keep yourself safe and away from medical complications.
Resources:
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/8874-traumatic-brain-injury
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/traumatic-brain-injury/symptoms-causes/syc-20378557#:~:text=Traumatic%20brain%20injury%20usually%20results,affect%20your%20brain%20cells%20temporarily.
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/traumatic-brain-injury/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20378561
https://www.cdc.gov/traumaticbraininjury/index.html
https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/traumatic-brain-injury
https://www.ninds.nih.gov/health-information/disorders/traumatic-brain-injury